
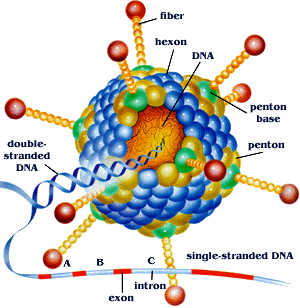
Oncoviral infections are common, but these infections rarely result in cancer. One or more extra insults, such as chronic environmental mutagens, immunosuppression, and inflammation are essential for cancer growth. Additionally, viruses are only an unconditional requirement for oncogenesis in Kaposi sarcoma and cervical cancer. Onco-viruses are divided into direct or indirect carcinogens, even though some overlay exists between the distinctions. Direct carcinogenic viruses have viral oncogenes that directly donate to neoplastic cellular transformation, whereas UN-planned carcinogens cause chronic inflammation which can lead to oncogenic transformation. Oncogenic DNA viruses like hepatitis B virus (HBV), human papillomavirus (HPV), EVB, human herpesvirus-8 (HHV-8), and Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV). Oncogenic RNA viruses contain hepatitis C virus (HCV) and human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 (HTLV-1).